With Huge Search Area Mapped, MH370 Hunt Resuming
 After a four-month hiatus, the hunt for Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 is about to resume in a desolate stretch of the Indian Ocean, with searchers lowering new equipment deep beneath the waves in a bid to finally solve one of the world’s most perplexing aviation mysteries.
After a four-month hiatus, the hunt for Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 is about to resume in a desolate stretch of the Indian Ocean, with searchers lowering new equipment deep beneath the waves in a bid to finally solve one of the world’s most perplexing aviation mysteries.
The GO Phoenix, the first of three ships that will spend up to a year hunting for the wreckage far off Australia’s west coast, is expected to arrive in the search zone Sunday, though weather could delay its progress. Crews will use sonar, video cameras and jet fuel sensors to scour the water for any trace of the Boeing 777, which disappeared March 8 during a flight from Kuala Lumpur to Beijing with 239 people on board.
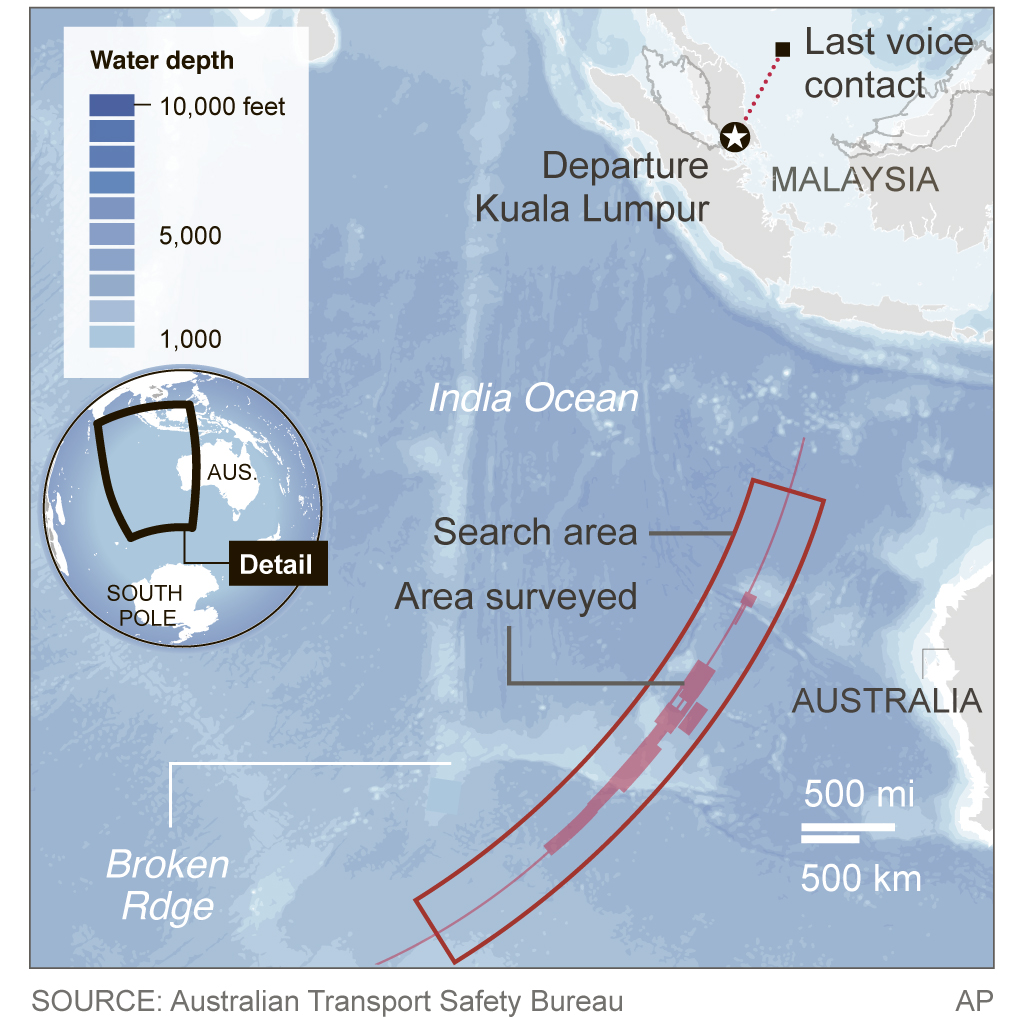
The search has been on hold for months so crews could map the seabed in the search zone, about 1,100 miles west of Australia. The 23,000-square mile search area lies along what is known as the “seventh arc” — a stretch of ocean where investigators believe the aircraft ran out of fuel and crashed, based largely on an analysis of transmissions between the plane and a satellite.
Given that the hunt has already been peppered with false alarms — from underwater signals wrongly thought to be from the plane’s black boxes to possible debris fields that turned out to be trash — officials are keen to temper expectations.
“We’re cautiously optimistic; cautious because of all the technical and other challenges we’ve got, but optimistic because we’re confident in the analysis,” said Martin Dolan, chief commissioner of the Australian Transport Safety Bureau, the agency leading the search. “But it’s just a very big area that we’re looking at.”
That area was largely unknown to scientists before the mapping process began in May. Two ships have been surveying the seabed using on-board multibeam sonar devices, similar to a fish-finder. The equipment sends out a series of signals that determine the shape and hardness of the terrain below, allowing officials to create three-dimensional maps of the seabed. Those maps are considered crucial to the search effort because the seafloor is riddled with deep crevasses, mountains and volcanoes, which could prove disastrous to the pricey, delicate search equipment that will be towed just 330 feet above the seabed.
This article appeared in print on page 42 of edition of Hamodia.
To Read The Full Story
Are you already a subscriber?
Click "Sign In" to log in!

Become a Web Subscriber
Click “Subscribe” below to begin the process of becoming a new subscriber.

Become a Print + Web Subscriber
Click “Subscribe” below to begin the process of becoming a new subscriber.

Renew Print + Web Subscription
Click “Renew Subscription” below to begin the process of renewing your subscription.







